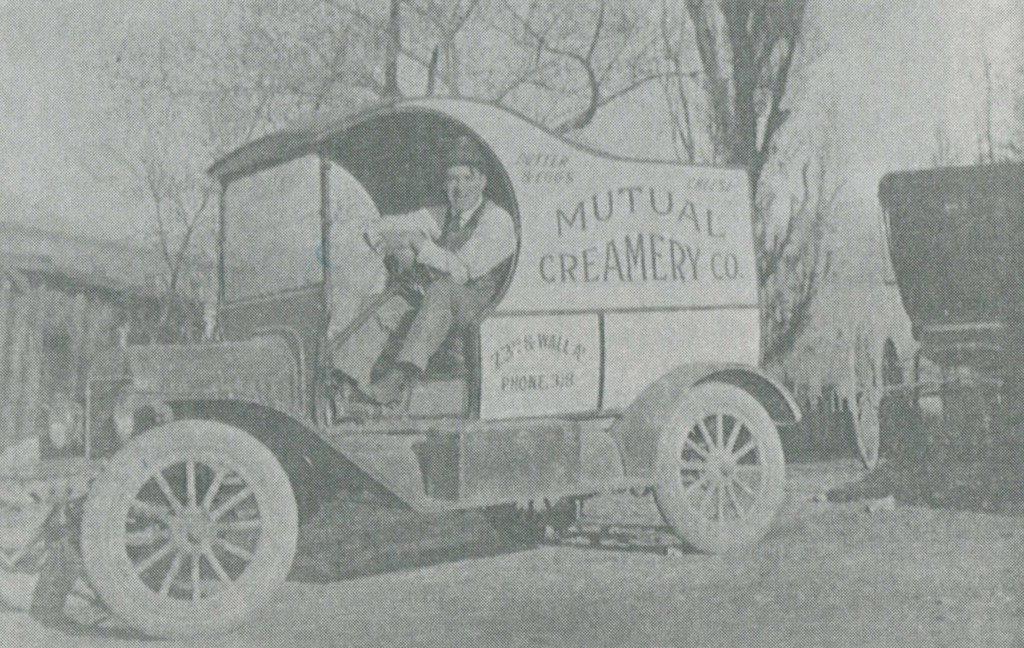
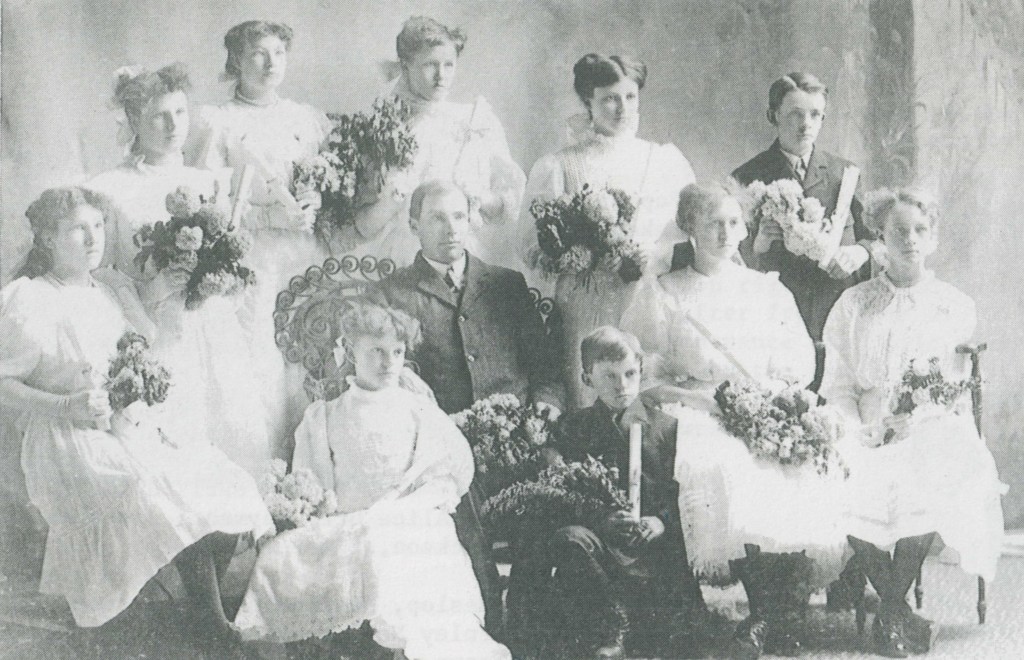
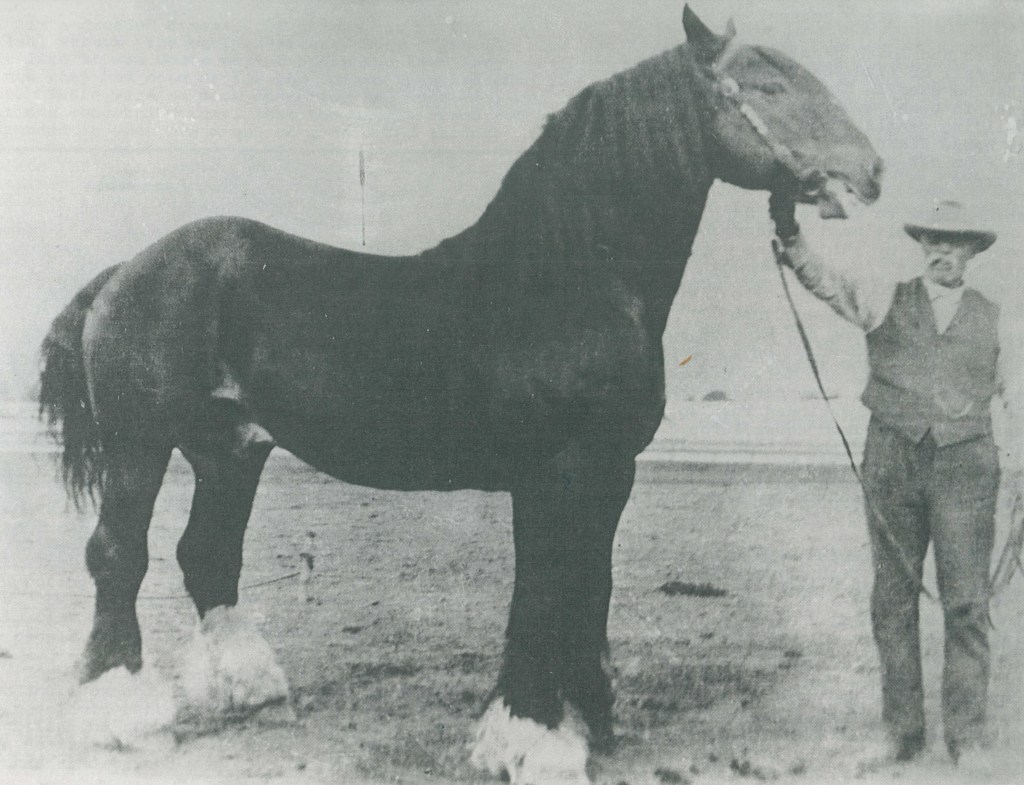
I stumbled upon this history written about Anna Elizabeth Reber. Anna was the third spouse to my John Christoph Nuffer. He married her 28 September 1893 in the Logan Utah Temple after my 3rd Great Grandmother Eva Katharina Greiner died 26 February 1893 in Mapleton, Franklin, Idaho. I thought it was interesting to review the life of a later spouse for John Christoph Nuffer. If you would like to review the pdf with pictures and more, it is attached here: Reber
The Story of Anna Elizabeth Reber
We would like to acknowledge dedicated genealogists who have preserved for decades the oral histories, journals, and handwritten records used in this story.
Faith and Courage
The Story of Anna Elizabeth Reber
By: Christine A. Quinn and Sterling D. Quinn
Graphic design by: Michelle Quinn, Au.D.
2017

Anna Elizabeth Reber
Early Years in Switzerland
1855-1875
Frau Reber felt only gratitude that her new baby was alive and had not died as had her last child. This little girl, born May 17, 1855, would complete their family of three sons and three daughters. They named the child Anna Elizabeth to distinguish her from her older sisters, Anna and Barbara. Later in life this child would come to be known simply as “Annie.”
The family was settled on the Reber’s ancestral farm in Schangnau, Bern, Switzerland where they spoke a unique Bern dialect of Swiss German, or Schwyzertutsch (Luck 1985). It was a small country village dotted with chalets, settled in the forested and fertile Emmental valley along the Emme and Aare rivers. It has been said, “An who have wandered through such magnificent forests as those of …Emmental, will never forget the berries, the mushrooms, the neatly arranged stacks of firewood, the beautifully colored autumn foliage, and the grey low-hanging mists and frost-decorated conifers of early winter” (Luck, 1985 p. 470). For hundreds of years in this valley the same industrious group of families had raised cattle for milk and cheese, while nurturing vineyards, orchards and crops.
This was a Switzerland just emerging from the hated status of a vassal state to the French Emperor Napoleon, an indignity thrown off seven years prior. Hope arose as the impoverished and beleaguered people named the central city of Bern to be the capital of the new Swiss Confederation (Luck) 1985).
The child Annie grew nurtured in the love of her family. Little girls in Switzerland wew taught the virtues of being clean, neat, punctual, thrifty, independent, and hard working. There were cows to be milked as well as household chores to be done. Annie would have been taught to knit and sew the linen, silk, and cotton fabrics for which the Swiss were famous. Education was also encouraged.
Tragedy visited the family when Annie’s 21 year old brother, Jacob, died in the fall of 1861. This loss left an indelible impression on the six year old girl, enough that many years later she ensured saving ordinances were performed on his behalf in a temple of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS).
Marriage and Family
1875-1890
How Annie and her future husband, Gottfried Weiermann, met is a mystery, but Bern did enjoy the reputation of being “more lively and sociable than any other town in Switzerland”. Men and women came together to amuse themselves with English country dances as well as waltzes (Luck, 1985 p. 255)
The Weiermann family worked the land and raised cattle for many generations in the village of Wynigen, a little over 20 miles northeast of the city of Bern. Rather than compete with five brothers for farmland, Gottfried decided to try his hand at the ancient profession of stone masonry. At age 23 when he met Annie, he had perhaps finished his apprenticeship and therefore gained some freedom to marry.
The couple were likely wed in the Protestant church in Wynigen on 21 August 1875. At the time, Annie was only months away from giving birth. The couple affectionately named this child after his father, Gottfried, but he was known as “Fred”. Although he was a sickly child, Fred would survive to bring his mother much joy and comfort until the end of her life.
Less than two years later the family moved again to Ferenberg where Anne gave birth to twins, Andre and Peter. They survived only a day, which tragically was not uncommon at that time as one out of every five births in Switzerland ended in death (Luck, 1985).
A year later Gottfried moved his family closer to the city of Bern to Ostermundigen, the largest regional quarry center in Switzerland. A special train with a cog in the center had been invented six years earlier to haul the thick, soft, and colorful sandstone up from the mines. Previously this job relied on horse or mule tams. The train made it possible to quarry enough stone for export, while also enabling urban expansion of Bern, which demanded massive amounts of stone for new buildings. Up to 500 men were working as either quarry men, Steinbrecher, who extracted the stone, or stone masons, Steinhau, who skillfully dressed, shaped, and cut the stone. Of the two, stone masons enjoyed a higher social status. The stone masons of Bern had an established fraternity in the city since 1321 (Storemyr, 2012). Gottfried, along with other craftsmen, flocked to this bountiful source of work.
Next to the noisy and dusty train yard, families of stone masons resided in multistory slums (Storemyr, 2012). Laundry hanging between tenements flapped in the wind while the narrow dirty streets teemed with children of all ages. Families crowded into tiny, tightly packed rooms, sharing limited sanitation facilities. “The wages were exceedingly low and people extremely poor” (Stucki 1888, Nov. 20). Stomachs were never full. In 1876, Swiss families were spending 60 % of their income on food. “A typical diet for the older children and adults consisted of coffee, black tea, or cocoa water with a little milk, some cheese and bread. ….The midday meal typically consisted of boiled potatoes, pasta, cheese, and coffee or tea, and wine. The evening meal was usually of cheese and a vegetable soup – the latter being made by boiling together leeks, cabbage, beetroot, potatoes, and pasta” (Luck, 1985, p.p. 249,441).
In the spring of 1878 with the aid of a midwife, 23 year old Annie gave birth to a son, Christian, and in September of the next year to a daughter, Ida. Like all their neighbors, the family fought for financial survival. Not quite 4 years old, Fred would have been responsible for helping keep his little sister safe and happy as their mother cared for her new infant. Imagine her efforts in washing cloth diapers and keeping a clean house under those circumstances! Years later Annie’s daughter, Ida, reflected her mother’s standards when she said, “Just because you are poor, you don’t need to be dirty” (Arave, 2017).
The Weiermanns had lived in Ostermundigen at least five years when on 2 August 1883 they welcomed a blonde curly-haired baby boy into their home. He was named Jacob after his maternal grandfather and deceased uncle.
Two years later Annie was expecting a child for her final time. Due to unknown circumstances (perhaps poverty or a medical crisis), she traveled an hour to the hospital in Bern on a cold December day in 1885 where she gave birth to a small girl who didn’t survive (Weyerman, G). They named her Anna.
At this point, the family consisted of Gottfried age 33, Annie age 30, Fred age 10, Christian 7, Ida 6, and Jacob age 2. Gottfried may have occasionally taken his oldest son to the stone yard to teach him aspects of his craft, because in later years Fred was known as a skilled stone mason (Weyerman G).
Gottfried’s pursued recreation of heavy drinking with the stone mason’s fraternity began to affect the Weiermann family. Workers bonded over alcohol, and Ostermundigen quarry men became legendary for schnapps consumption (Storemyr, 2012). Unfortunately, Gottfried’s drinking created a fissure in his marriage. Circumstances only worsened with the death of 10-year-old Christian on 4 June 1887. The cause is unknown; it may have been an accident, or one of the many infectious diseases rampant at that time such as influenza, smallpox, diphtheria, tuberculosis, Typhus fever, or measles (Luck, 1985).
Annie and Gottfried’s marriage soon reached a breaking point and ended in divorce (Weiermann, I. 1955). Years later in a heart-wrenching remembrance, Fred wrote, “My parents lived financially poor. Conditions brought it about that the family got badly broken up and scattered. Three of my brothers and one sister was called on the other side. In the year 1887, the rest of my family met the sad experience of the separation of Father and Mother on account of drunkenness” (Weyerman, G).
Desperate to provide for her children, Annie hired out as a seamstress, one of the few professions available to women that would allow her to care for little ones at home (Wheeler, I.). Wages were notoriously low; a decade later, women making shirts in their homes were earning less than a penny an hour, and often worked more than 12 hours a day (Cadbury, 2011). Bending over and straining to see tiny stitches by the dim light of an oil lamp was exhausting. “As one of the infamous sweated trades, seamstressing represented the trails of arduous work, miserable working conditions, impossibly long hours, and equally impossibly low wages” (Harris, chap. 2.). The older children most likely helped their mother by doing the chores and mining their siblings; but life soon changed for 11 year old Fred in a way that must have torn at his mother’s heart.
Because of the family’s poverty and her status as a divorced mother, Annie was legally compelled to register with one of the councils in Ostermundigen responsible to care for the poor and orphans. If it was believed the children could not be provided for this council had the power to break up the poorest families. Despite Annie’s courageous efforts to support her children, the council forced Fred to enter into foster care, there he became known as a “Verdingkinder”, or literally “discarded child” (Foulkes, 2012).
In this sad circumstance, the amiable and music-loving Fred was taken from his mother and given into the custody of a gentleman who lived in Habstetten, about an hour’s walk from his family. There, Fred attended school and helped with the chores. He longed for his family, and visited his mother whenever he could obtain permission (Weyerman,G).
“Oh! But for one short hour!
A respite however brief!
No Blessed leisure for love or hope,
But in their briny bed
My tears must stop, for every drop
Hiders needle and thread!”
With fingers weary and worn,
With eyelids heavy and red,
A woman sat in unwomanly rags,
Plying her needle and thread —
-Thomas Hood
“Song of the Shirt”
Within a year after these turbulent events, Annie received an invitation from her neighbor to meet with missionaries, or Elders, from LDS church. Members of this faith were commonly known as Mormons. After meeting several times, Annie began to take her children along to Sunday School and other meetings (Wheeker, I). Annie almost immediately recognized the simplicity and truthfulness of the long awaited and newly restored church of Jesus Christ. Her countrymen had been searching for this truth through the Protestant Reformation for over 300 years (Luck, 1985). One can imagine the gospel of Jesus Christ calming her soul and assuaging her fears at a time of life when it was most needed.
Annie, Ida, and Jacob began a formal study of Mormonism with young Elder Alfred Budge, who taught them the first principles of the gospel (Weyerman, G). Annie may have read the tract, Die Froke Botschaft, (Glad Tidings of Great Joy), or Glaubenskekenntniss, (The Articles of Faith) (Reiser). In time, she received a witness from the Holy Ghost that Christ’s church had been restored to the earth through the young American prophet, Joseph Smith Jr. Despite some local persecution, she and Ida were soon converted and baptized by Elder Budge in late October 1888. At this time, Jacob had not yet reached the age of 8 years old required for baptism (Wheeler, I).
Arriving at church on Sundays took an hour of walking into downtown Bern, where Annie and her children wound through cobblestone streets lined with ancient stone houses standing side by side like soldiers at attention. They knew they were getting close to their destination when they heard the Sabbath bells pealing from the gothic tower of the Bern cathedral. Soon they arrived at the mission office where church services were held. The many families who attended the Bern Branch may have eaten a modest lunch as the fellowshipped between morning and evening meetings. Every week the congregation took the sacrament and listened to preaching by either Mission President Stucki, the local Branch President, or one of the Elders. A volunteer choir provided uplifting music (Stucki, 1837-1918).
Around this time Fred went to live with another foster family in the closer town of Ittigen, which shortened the walk to see his loved ones. During Fred’s visits, his mother earnestly shared with him the principles of the new religion she was learning. It was her heart’s desire that he would be baptized and join the church.
Swiss/German
Missionaries
1880-1890
The Mormon missionaries in the region of Bern were led by John Ulrich Stucki. A native of Switzerland, Stucki had been living in the territory of Utah at the time of his assignment to serve as the Swiss/German Mission President. This would be the second time he accepted this weighty responsibility.
Not only would Stucki be responsible for the 13 traveling Elders in the mission; he would also publish the monthly LDS newsletter, “Der Stern”, and he would administer from his office in Bern all the branches of the church in Germany and Switzerland. Added to these weighty responsibilities was overseeing the twice yearly emigration to Utah made by Swiss and German Mormons. These members wishing to join others of their faith in the building up of “Zion” would leave their homes and travel to the Rocky Mountains of the United States of America (Stucki, 1837-1918).
Accompanying Presiden Stucki to the mission field was 19 year old Alfred Budge, the son of Stucki’s good friend, William Budge. What thoughts and anticipations might have filled the young elder’s mind as he contemplated his father’s earlier mission to Switzerland in 1854, “when opposition to the church was so violent that within three months he was on thirteen occasions placed under arrest and imprisoned for short periods, and finally was obligated to return to England!” (Budge, W).
When President Stucki and Elder Budge arrived in Switzerland on 15 May 1888 Elder Budge did not speak German (Stucki, 1837-1918). Five months later he was teaching the Weiermann family in Ostermundigan using their native tongue (Wheeler, I).
Working with Elder Budge was the pleasant-mannered Elder Albert Schneider Reiser from Salt Lake City. His Swiss parents spoke German at home, so he had the advantage of being familiar with the language.
Seventeen old Albert had been forced to grow up fast after his father, along with many faithful LDS men, was incarcerated by the United States government for the common practice of polygamy. To support his family, Albert took charge of their clock repair business in downtown Salt Lake. He delivered customers’ clocks to the prison, where his father repaired them. Interestingly, Elder Budge’s father was converted to the LDS faith in Scotland, and Elder Reiser’s in Switzerland; yet they both emigrated to America on the same ship and crossed the plains to Utah in the same wagon train 28 years earlier in 1860 (Reiser).
Switzerland to United States
Emigration
1890
Elder Reiser arrived in Switzerland just a few days after Annie’s baptism, and began helping to teach the Weiermann family (Stucki 1837-1918). The missionaries had with them some pictures of Utah. For decades, Mormon converts in Europe had been encouraged by church leaders to gather to “Zion” in the American West. Surely ideas of emigration were planted by visiting Elders and church officials, but when accused of being an emigration agent, Elder Reiser remarked: “It was not my business to persuade people to emigrate, but to bring them the Gospel….there was only one true church….[I] told them how important it was for mankind to investigate Joseph Smith’s message….”(Reiser).
One late summer morning Fred joined his family on their brisk walk to church. His mother made an astonishing announcement that she had arranged for them to emigrate to Zion! Because the children had received an inheritance from the death of their father’s Aunt Isali, they could afford to emigrate. The family would be reunited and travel together to start a new life with the Saints in Utah. (Weyerman, G.)
After the day’s church services, Annie shared with the mission president some of her worries about Fred’s situation. President Stucki lovingly took hold of her hands and prophesied, “Fear not, for your son Gottfried. He will be the means of bringing many souls into the church” (Weyerman, G). Within 10 days, Annie and her three children, led by President Stucki and joined by Elder Budge, began their odyssey to Zion.
The miracle of emigration did not take place without Annie’s heroic effort and faith. President Stucki promised that if the saints paid their tithing, a way would be opened up for them to join the saints in Zion (Stucki, July 31, 1888). The children’s inheritance from their great aunt had been put into an untouchable trust. With nerve and steely determination, the slight-built Annie faced authorities and requested they give her the funds to use for emigration to America. When they refused, she threatened to leave without the children and then the state could raise them! After this ultimatum, they relented and granted her the inheritance of 500 Swiss francs (Weiermann, I., 1955).
Annie delivered the money to President Stucki, who hired agents from the Guion shipping line to purchase train and steamer tickets. These agents arranged transportation, loding, and food, and also oversaw the moving of luggage from Switzerland to England and then on to America. President Stucki also took care of details such as procuring bedding, tinware, etc. to be forwarded to the steamer for the transatlantic crossing (Stucki, 1937-1918).
In preparation for the voyage, Annie made some traditional hard dry Swiss bread, then fried it in butter to be their principal diet. The missionaries taught them how to say “hot water” in English, so they could request some to pour over their bread, thus making it edible (Wheeler, F 1948). Then the family of four packed all their worldly goods into five pieces of luggage (Mormon Migration). They were now ready to travel over 5,000 miles to join the Saints in Utah.
“May God Bless Them All and Bring
Them Safely into the Bosom of the
Church and Kingdom of God”
This was the fourth and final emigration that President Stucki oversaw during this mission. He and Elder Budge wew being released from their callings to return home to America with the emigrating saints. Feelings were tender in the Bern branches the day before departure when President Stucki preached his farewell sermon in Sacrament Meeting. Since his arrival two years earlier, he served the saints daily while surviving fever and smallpox. At the close of the meeting it is likely they sang the Swiss hymn, “May God Bless Them All and Bring Them Safely in the Bosom of the Church and Kingdom of God” (Stucki, 1837-1918).
The next morning, Monday, 1 September 1890, Annie (35), Fred (14), Ida (10), and Jacob (7) began their pilgrimage by boarding the train in Bern. Who can know the conflicted feelings that must have been in their hearts? These may have involved jow, excitement, and hope of a new life in America among the Saints of God; mixed with the regret of leaving loved ones and the magnificent country of their birth. Years later when Fred saw a newsreel about the Alps in Switzerland he sat and wept from homesickness for his native land. He commented, “The beauty of that land could not be found anywhere else”. (Weyerman, G).
At 10:30 a.m. the saints were on their way north to the border city of Basel entertaining themselves with singing. Arriving after noon, the train pulled into Basel to pick up the missionaries as well as 13 members of the faithful Gygi family. To everyone’s horror Rudolph Gygi, the father, had been stabbed the night before in the face by a mob of hoodlums who thought he was taking his six daughters to be enslaved in polygamy (Gygi).
Through the night and into Tuesday, the travelers continued north by train into Belgium. It was 2 September, Ida’s 11th birthday. Perhaps she made friends with Anna and Elisa Gygi and helped them watch their younger brothers and sisters. At the late hour of 11:00 p.m. the weary saints arrived in the port city of Antwerp. The Swiss emigrants were met at the train station by their agent who provided a wagon to transport their luggage and at least seven children under age 10 to a boarding house. Before retiring, all received refreshment, which could have been soup, meat, vegetables, coffee, and bread (Stucki, J. 1837-1918).
After a night’s rest, the Swiss saints united with about 51 emigrating converts from Germany who spoke German so differently that neither group could understand the other. Together this made 72 travelers. Once again they loaded their belongings onto a wagon to transport them down to the dock where the shop was moored (Stucki 1937-1918.) There the family had their first glimpse of the vast sea and all the ships and business of the bustling Antwerp harbor. Searching for words, Ida wrote as an old woman, :The trip across the ocean was quite – I don’t know what you would call it – an experience to us” (Weiermann,I. 1955).
All boarded the steamer, which launched into the North Sea shortly after noon. Their destination was the port of Hull on England’s eastern shore (Woods & Evans 2002). For many, this was the first time on the open sea. Spirits were high and the saints passed time with singing hymns of praise, or conversion pleasantly. President Stucki recorded, “the vessel went steady, sea sickness was therefore very light and confined to but few” (Stucki 1837-1918).
They traveled all night to reach Hull on Thursday at 3:00 in the morning. The ship could not dock at low tide, so the passengers had to transfer in the dark to a tugboat that took them to shore. Ida remembered the confusion, “While crossing the North Sea, something went wrong with the ship and we had to change ships. Somehow we lost a roll of bedding, which we needed very much” (Stucki 1837-1918) (Weiermann, I., 1955). Despite the hassle of getting ashore, the emigrants were met by a kindly agent who examined their luggage to verify it was duty-free. He also saw that the hungry Saints received something to eat before boarding a train late in the day.
Lulled to sleep by the clicking -clacking rhythm of the steam train’s wheels, the adventures slept most of the six-hour 140 mile journey across England to Liverpool. They arrived before dawn on Friday morning (Stucki, 1837-1918).
September 1890
MON 01 Train: Bern – Basel
TUES 02 Train: Antwerp
WED 03 Boat: Antwerp – Hull
Thurs 04 Train: Hull – Liverpool
FRI 05 Liverpool – Immigration House
SAT 06 Loading of the ship, off at 3pm
SUN 07 Atlantic Crossing Day 1 – Queenstown
MON 08 Atlantic Crossing Day 2 – 294 miles
TUES 09 Atlantic Crossing Day 3 – 300 miles
WED 10 Atlantic Crossing Day 4 – 320 miles
THURS 11 Atlantic Crossing Day 5 – 298 miles
FRI 12 Atlantic Crossing Day 6 – Newfoundland
SAT 13 Atlantic Crossing Day 7 – 314 miles
SUN 14 Atlantic Crossing Day 8 – 320 miles
MON 15 Atlantic Crossing Day 9 – 298 – miles
TUE 16 Atlantic Crossing Day 10 – 308 miles
Arrival in New York, USA
WED 17 Luggage and Customs
TRAIN CROSSING TO UTAH & IDAHO
SUN 28 Train: Montpelier, ID
Wagon and Buggy to Paris, ID
Once again, shipping hires by President Stucki greeted the Mormon converts upon their arrival to Liverpool. This city situated on the western coast of England was considered in the nineteenth century the most active international port of emigration in the world. It was also home to the British Mission, and served as the administrative headquarters for the LDS church in Europe (Woods & Evans, p.91).
Passengers were not allowed to board their ships until either the day before or the day of departure (Liverpool); thus, the saints were taken to an immigration house to wait, eat, and rest for a day (Stucki, 1837-1918).
Meanwhile, it was LDS church procedure that every emigration company have a Presidency. They would watch over the saints, conduct Sunday services, and see that everyone reached their destination. John U. Stucki acted as President, and selected Alfred Budge and C. Meyer as his counselors. The day before departure, they were called and set apart by the British mission president, George Teasdale (Stucki, 1857-1918) (Mormon Migration Database, 1890, Sept. 6).
The sleek 366.2 ft steamer S/S Wisconsin, piloted by Captain Worral, waited patiently at port to receive her passengers (Mormon migration database, 1890, Sept. 6). She was one of a fleet of 16 ships run by the Liverpool and Great Western Steamship Company, known commonly as the “Guion Line.” For 20 years the company’s ships had been launching twice a week to transport passengers and mail from Liverpool to New York. A typical trip across the Atlantic took a week. At a time when there was no air travel, they were known as “ocean greyhounds” (Guion) (Miller).
All day Saturday September 6 a steady stream of humanity carting trunks, baskets, bags, and bed rolls trudged up the ramp of the stately steamship with its tall dark smokestack. Seventy-six first staterooms as well as spacious dining rooms. Thy were joined by 100 intermediate passengers.
Then the Weiermann family joined a mass of 800 impoverished voyagers crowded into the notorious “steerage” section below deck (miller). Annie, Ida, and Jacob were together in the Port Aft Steerage, while Fred was assigned Fore Steerage, perhaps because he was an older single male (Mormon migration Database, 1890, Sep.6).
It was a cacophony of humanity: men women and children from many countries speaking a babble of languages. Each passenger was assigned a number on a canvas berth. When not in use the berths could be neatly stowed away making space for tables and seats during the day. The journey would be no luxury cruise for these steerage passengers. Conditions were cramped, food was poor, and the atmosphere often bad; especially during rough weather when access to the upper deck was restricted. (Solem).
By 3:00 PM the ship’s crew drew up anchor. All passengers went on deck, waving white handkerchiefs and throwing hats as they watched England slowly shrink into the horizon. With this fanfare, Annie and her family bid farewell to their old life, and looked with hope to a brighter future in America, the land of opportunity.
As the ship glided into the night, the Swiss converts completed the irs six days of their traveling adventure. When the sun came up it was a beautiful morning and the sea was as smooth as glass. President Stucki would have liked to conduct Sunday services, but the ship was too crowded and there was nowhere they could meet without disturbing someone.
By Late morning they reached the southern seaport of Ireland’s Queenstown harbor, where they remained for an hour or so to pick up more passengers. Soon after moving out, they were engulfed in a dense blanket of fog. Everyone listened with suspense to a shrill whistle blow in rapid succession waning other floating vessels of their presence. Soon all was well as they glided out of the fog into weather as fine as before. Although the steamer was quite steady, some began to get sea sick (Stucki, 1837-1918).
By Monday, several of the women and a baby were pretty sick, which kept President Stucki and his counselors busy. Ida and her brothers were focused on the adventure and didn’t seem to mind the discomforts of travel. She said, “We used to go up on deck all the time. The sailors would take us skating across it. We really had a good time – us kids did when we wasn’t sick” (Weiermann, I., 1955).
If the passengers weren’t sick on Monday, many became queasy on the next day when a wind made the sea rough and caused the ship to pitch and roll.
An English convert traveling a few years earlier on the same ship described a similar chaotic event:
“….Towards night the wind began to raise rather rough and the captain shouted out from the upper deck, “Look out for a storm.” The sailors began to run from one end of the ship to the other with large chains and ropes….We was then all ordered down below. Pots, pans, buckets, and everything that was not fast was rolling about. Old people falling down, young ones laughing at the fun but did not last long. A large rope had been placed all along the water closets for protection. During the time we was standing by this rope waiting to get in the closets, our ship gave another sudden roll and we fell over this rope, old and young, head and tail together, vomiting on each other. Girls screaming, boys laughing, old men and women grumbling, children crying” (Horsley, S., 1877, September 19-29).
The Ship continued to roll heavy with water pouring over the deck clear into Wednesday. Soon even President Stucki and Elder Budge were sick too (Stucki, 1837-1918.) Years later Ida recalled, “When we were sick we would have to go on deck every day no matter how sick you were. But we got across” (Weiermann, I. 1955).
On Thursday quite a number of suffering women remained in their berths. Crowded conditions below deck caused the air to become fetid with disagreeable body odors, strange foods, vomit, waste, and ship oil. Mercifully, the temperatures were quite cool (Stucki, 1837-1918).
By the sixth day at sea the weather improved, the ship steadied, and everyone felt much more cheerful. Despite the rather chilly stiff breeze most passengers enjoyed a refreshing interlude basking in the sun on deck. Some excitedly observed an iceberg silhouetted against the horizon about ten miles to the left (Stucki, 1837-1918).
At last after being a sea for a week, the ship entered cal waters off the coast of Newfoundland. Some of the sick were beginning to feel better; everyone felt happier and more hopeful. In the afternoon, steerage passengers had to pass a routine health inspection, and if necessary receive vaccinations. This was in the interest of the shipping company to avoid paying a hefty fee for any unhealthy passengers.
Sunday, President Stucki conducted church services in he saloon, or the first class public area of the ship. The next few days passed without incident. There was some rain, but much to the passengers. President Stucki notes in his journal, “If it had been as warm all the way as the first two days, there would no doubt have been a good deal of sickness; the Lord is overruling all things for good.” (Stucki, 1837-1918).
On Tuesday afternoon, to everyone’s great joy and anticipation,their destination was sighted! All the immigrants strained to see the fabled America. With gratitude and relief for a safe journey, the travelers watched the New York skyline slowly grow into view. Their hearts certainly swelled at the first glimpse of the magnificent and newly erected Statue of Liberty. Majestically she lifted her lamp to greet the “huddled masses yearning to breathe free”. (Lazarus, 1883). They passed Staten or “Quarantine” Island at 5:00 that evening, pulling up to the pier at 7:15 p.m. It was 16 September 1890; the first day of their life in America!
Heavy rain caused some delay the next day, but the baggage was unloaded by Wednesday noon, and an examination made by custom house officers. Since the Immigration Station on Ellis Island was under construction, new arrivals were taken to the temporary Barge Office located in Castle Clinton at Battery Park on the southern tip of Manhattan Island (Ellis Island Immigration Museum.) There all steerage passengers had to pass inspection or be sent back. Ida years later remembered the tense time in this way, “When we arrived at Ellis Island (sic), [mother] did not have the necessary amount of money the government required of those coming into this country, so she showed them a letter of proposal of marriage she had received from a convert who was already in the United States, and let them believe she was coming to marry him” (Weiermann, I. 1955) (Wheeler, F., 1948).
When all was cleared and the immigration process finished President Stucki concluded in a letter, “We are very thankful to our Heavenly Father for the many blessings received thus far, and feel to trust in him for our safe arrival in the land of his choice” (Mormon Migration database 6 Sept. 1890-Sept. 1890.).
It isn’t known for sure which railroad route the Weiermann family and their fellow saints took west. Nevertheless as they crossed the continent, vast flat prairie lands would seem endless to someone from a tiny country encircled by tall mountains. It was an adventure with pleasures for wide-eyed travelers. Ida thrilled to see wild horses running with the train (Wheeler, I., 1955). Fred with gratitude recorded, “We had good health and lots of pleasure on our journey both on train and ship”. (Weyerman, G).
Most of the European immigrants were destined for the Utah towns of Salt Lake City, Provo, Payson, Logan, and Nephi. About 21 of the weary saints stayed on the train to travel northwest into the new state of Idaho. They arrived in the frontier town of Montpelier on 28 September 1890. Continuing on by wagon and buggy, the Weiermann family, returning missionaries, and others rolled 10 miles south to the tiny town of Paris, Idaho. Fred remembered, “Elders Stucki and Budge were also glad to get home and and had all things arranged for hospitality.” (Weyerman, G) (Stocker, J).
In Paris, the red sandstone of the newly dedicated tabernacle looked down on the little town. This recently settled country of small farms was very different from the noisy crowded city the Weiermann’s were used to. However, for Annie it may have triggered happy memories of her youth growing up in rural Switzerland.
Life in America
1890-1893
One of the great motivations for Mormon emigration was to be able to reach a temple, considered the “Lord’s house,” where they could receive ordinances necessary for their own salvation and perform them by proxy on behalf of their deceased ancestors. This was a priority which Annie acted on immediately. It is recorded that her 10 year old son, Christian Weiermnn, three years deceased, was baptized by proxy in the Logan, Utah temple on 25 September 1890, suggesting someone took his name to the temple before the family finished their journey to their new home in Idaho. (Proxy baptisms were not required for her twin sons and daughter, since they died as innocent infants).
Many people who came to the United States chose to change or “americanize” the spelling or their names. Fred’s Posterity most often spell their name Weyerman, while the family of Ida has most often spelled their name Weiermann. In various family records the name can be seen in old records; Gottfried was known as “Fred”, his brother Jacob sometimes as “Jake”, and their mother, Anna Elizabeth, came to be known as “Annie” (1900 census).
Soon Annie and her young son Jacob moved into a rented log cabin owned by a Mrs. Herzog. Annie began earning money taking in sewing. Ida had the opportunity to live with and work for the beloved Stucki family, who were also boarding the local school teacher. Ida reminisces, “My teacher lived at the Stucky (sic) home and was very good to help me with my lessons” (wheeler,I., 1955). Once again, Fred boarded away from his family when he went to work on a farm.
Paris, Idaho had been colonized by the Latter-day Saints 17 years earlier and had two LDS wards. What a change after attending the small branch in Bern! It was wonderful to dwell without persecution among people who believed and lived as they did; however, life was not without challenges. Everyone had to work hard on the frontier for the survival of their family. It wasn’t easy learning a new language and adjusting to the ways of America. For example the young Swiss girl, Elisa Gygi, whom Ida certainly made friends with on the journey to Utah, recalls how at school she was told her name was to be the more familiar Alice instead of Elisa. The children made fun of her because her shoes and clothes were different. Subsequently, Elisa took turns with her sister wearing to school a nice dress and some shoes someone gave them. In their poverty the Gygi family happily received groceries, clothes, and candy for Christmas from the Bishop of their ward (Gygi). It isn’t hard to imagine the Weiermann family relying on friends in a similar way until they were able to earn money to support themselves.
On 29 December 1890, several months after their arrival in Idaho, Fred received the ordinance of baptism into The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-Day Saints. Several days later, on New Year’s Day, his younger brother, Jacob, was also baptized. Then, according to the custom at that time for member immigrants arriving in Zion, Annie and her daughter, Idam, were rebaptized. It was a new year and a new life for the Weiermann family.
Fred traveled 20 miles north to Nounan, Idaho, to work. There he was also able to procure a log cabin for his mother and brother. Ida earned money by living in several homes where she helped with chores. Then she said, “Mother got work so I stayed at home the next year. Then we went back to Paris [Idaho} where mother met Mr Nuffer at a German Conference….” (Wheeler, I. 1955).
Family and Marriage
1893-1901

A medieval castle overlooks the southern city of [Neuffen], Germany, where 27-year-old Johann Christoph Nuffer married Agnes Barbara Spring early in the year of 1862. Four years later tragedy struck when within 7 months their baby girl and her 26-year -old mother died. Christoph was now left a widower to raise two sons, John, age 4, and Fred, age 3. (Nuffer, C).
A month later on July 25, 1867, he married Eva Katharina Greiner, who began to raise his sons as her own. Christoph and Eva were surrounded by their extended family, and were supported by Christopher’s work as a dress goods weaver and a salesman of produce from his vineyard and farm. Over a span of ten years, they added Regina, Charles, and Adolf to their family. (Nuffer, C).
After listening to the Mormon missionaries, the Nuffer family decided to join The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints. They secretly damned a millrace at the rear of the house so the family could be baptized at night, undisturbed by hostile villagers. To avoid the persecution that immediately followed, they decided to emigrate to Utah as soon as possible. Christoph sold their home and land, and borrowed money from another immigrating family to gather the needed funds. Notwithstanding all the children catching measles, the family survived the transatlantic crossing in May 1880 on the steamship Wisconsin. (Ironically, the very same ship that in ten years would bring the Weiermann Family to America) (Naef, 1990).
The Nuffers followed many German and Swiss saints who pioneered Providence, Utah, situated just south of Logan. Like countless others, they started our poor and worked hard to better their circumstances. Thankfully, the older sons Fred and John helped a great deal with the heavy labor. A year after arriving in Zion, their last child, Mary was born (Naef, 1990).
In the fall of 1883 the oldest son, John, persuaded his father to sell their home and move into southeastern Idaho to homestead. Two years later they set up another claim. It was a rough life, but his son Charles recalled, “(We) were happy and thanked the Lord for what we had. Mother would read a chapter from the Bible, we would have prayer an we would go to bed early….We thanked our Heavenly Father for what we had and lived by faith…a I remember we never got discouraged for we felt the Lord was on our side” (Nuffer, C., 1949).
The Nuffer ranch was located northwest of Mapleton, Idaho. Their farm was cut in half be the main road. On the east side was the land where their homes, stables, and fruit orchards were located. On the west side of the road was meadow blanketed in lush grass with a creek running through it. This farm from one end to the other was a beautiful place (Naef, 1990).
In the winter of 1893, Eva, Christoph’s wife of 2 years, developed pneumonia and suddenly died within a week. Her grieving family buried her in the first grave in the new Preston, Idaho cemetery. Christoph could not bear to be alone in the home where he had so happily lived with his wife, so his sons Charles an Adolf ran the farm, “while there father was away most of the summer at Bear Lake and other places” (Nuffer, C).
While away, Christoph, now known as Christopher, met 38 year old Annie Weierman at a German Conference (Wheeler, I., 1955). These conferences were an opportunity for German speaking LDS converts to socialize using their native language. Through uplifting sermons, singing and dancing the Conferences offered support for immigrants adjusting to their new lives.
By the end of the summer, Christopher and Annie knew they wanted to get married. They were sealed for Time and Eternity in the Logan temple a few months later on 26 September 1893 (Reber).
The one photograph we have of Annie was likely taken in Logan, “The Temple City”, at this time. She serenely gazes out of the image, an attractive women with light-colored deep set eyes, high cheekbones, fair smooth skin, and unusually sculpted lips. Her brown hair is modestly pulled back to the nape of her neck and wrapped into a bun. She is slightly built, probably no taller than her daughter who grew to about 5 feet 2 inches. Her newly learned English would have been graced with a lilting Swiss accent. She wears a dark tailored dress, which she may have sewn, that has a high collar and mutton sleeves, the height of fashion in 1893. It could be imagined the jeweled heart brooch pinned to her collar could have been a wedding gift from her husband.
At age 59, Brother Nuffer was considered “ an old widower” by Annie’s children. (Weyerman, G). Besides love and companionship, he offered their mother a social status and financial security that she had likely never experienced. Their stone house surrounded by pastures, orchards, and a garden may have reminded her of her rural youth in Switzerland. Because her new husband had lived in the area for many years, she benefited from the reputation he had in the community as a successful farmer. The Nuffer name was well known in the surrounding towns as Christopher’s oldest son, John, was a trained architect and stone mason. He helped build the Logan temple, and also designed many of the public buildings in Preston, Idaho; including the opera house, bank, and churches. (Nuffer, J).
Annie and Christopher had many things in common, such as firm testimonies that Joseph Smith had indeed been an instrument in the restoration of Christ’s church, and that they were building up Zion in the American west. They had both followed the same path of conversion, they both spoke German and understood the ways of the “old country”, and they both followed a strikingly similar emigration path. But like many second marriages, there was the potential for tension and competition for loyalty between their children. As can be imagined, the children and their mother were very close after weathering so many adversities together. Annie’s marriage to Mr. Nuffer may not have been favored by the children. Fred’s feelings were, “Ida and Jacob remained no longer with mother then, but had to look out for themselves, neither I had any place that I could call my home” (Weyerman, G).
During the next year, Fred Weyerman became engaged to a girl named Sally, but this arrangement ended abruptly when Sally eloped with another man. This seemingly devastating event turned out to be a blessing when Fred met 20 year old Olena Hoth while they were at a party of a mutual friend. Fred and Olena were married by their bishop two weeks later. “Lena” was raised in a faithful Latter-day Saint family. She was a loving, loyal, and hardworking woman who would have a special role in the life of her mother-in-law. She and Fred loved each other and eventually had a family of 15 children. (Weyerman, L).
Two months later the newly married Fred and Lena traveled a distance to the Logan temple to be sealed on 26 September 1894 for Time and Eternity. In preparation for his temple ordinances, Fred Weyerman was ordained an Elder by their beloved Swiss mission president, John U. Stucki. It was a joyful occasion as Lena and Fred received their endowments and were sealed together. (eyerman, G) Later that same day, Annie must have glowed with happiness as all her children were sealed to her and Christopher Nuffer (Reber, A).
About this same time Annie’s step son, Charles, recorded she made him temple clothes in preparation for his marriage. He reminisced that, “His new step mother was helpful to us in many ways as we began our married life” (Nuffer, C., 1949).
In 1895 Fred and Lena welcomed a baby and named her Anna Weyerman. Fred bargained with his stepfather for forty acres of his farmland in Mapleton, so Annie looked forward to seeing her new granddaughter often. (Weyerman, G).
Near this time, Christopher’s oldest son, John, left to serve in the German/Swiss mission. Imagine Annie’s feelings of curiosity and nostalgia as she read letters posted from the mission headquarters in Bern, Switzerland.
That winter Ida married David Wheeler. His father, Calvin Wheeler, was a notable pioneer who settled in the Mapleton area seven years earlier. David reminisces in his autobiography, “I finally met a girl, Ida Weiermann Nuffer, that I thought just suited me, and finally ask her to marry me. She wanted me to wait for a while but as I had got a call to go on a mission she finally consented. We married in the Logan Temple on December 4, 1895. Ida was just a few months past sixteen years of age.” David let six weeks later to serve a mission in the southern states of the USA. Ida supported herself by living with and working for families until he returned two and a half years later (Wheeler, D).
After a year of improving his land, Fred went to make a payment and fix the deeds; however, the sons of “Mr. Christoffer Nuffer would not agree, so [we] had to pull out with empty hands” (Weyerman, G). It could have been that the sons didn’t know about their father’s deal or agree with it. There was a lot of competition in the area over staking out claims on various parcels of land. Christopher’s sons had also been working the land for years with the hope of ownership. The emotions raised at that time may have prompted Ida to comment that “We, [Fred, IDa and Jacob], were not welcomed there” (Wheeler, I. 1955).
In the year 1896, Fred and Lena lost a baby named after Fred’s brother, Christian. In 1898 they also lost a month-old baby girl named Marie Weyerman. That same year Ida’s husband, David, returned from his mission. Also, Annie’s first husband and father of her children Gottfried Weiermann, died at age 46 in his home town of Wynigen, Switzerland (Wheeler, D.) (Reber,A).
David and Ida moved to the mountains of Western Idaho where David took a contract to cut railroad ties. On 28 December 1899 Ida gave birth to her first child, Florence, alone in a crude timberland shelter while waiting for a doctor to arrive. Ida’s only assistance was a blessing from the local missionaries, who afterward sent out into the yard to pray for her (Wheeler, I).
The last years of Annie’s life were marked by marriages, births, harvests, missions, and some deaths. Mostly it was the day-to-day rhythm of life that generously filled the calendar. After they sold their ranch to the Hull Brothers of Whitney, Christopher and Annie moved to Preston into a two-room frame house near his oldest son, john (Naef, 1990). The 1900 US Census records the family living in Preston, Idaho, and lists Christopher Nuffer as a farmer, Annie E. as his wife, and Jacob, his single stepson, as a farm laborer. It also notes that Annie can read and write English. Sometime between the 1900 Census and March 1901, Christopher and Annie Nuffer moved to Logan, Utah, which was to be their last home together (Naef, 1990).
By the time, Annie was very ill with “dropsy”, an old term for edema, or fluid retention usually in the feet, ankles and legs (Weyerman, L). She may have suffered from it for years as it could have been caused by congestive heart failure, diseases of the heart muscle, or some other heart ailment. As these diseases progress breathing becomes difficult; making walking arduous (Quinn, 2017).
Possibly because Annie needed someone stronger than her aging husband to nurse her, she moved in with her son, Fred. His wife, Lena, was two months from giving birth. This was a charitable and generous act on Lena’s part, as she was now caring for Annie, a baby and three other children under the age of 5. (Weyerman, L).
As soon as Annie’s daughter, Ida, recovered enough from the birth of her second child in August 1901, she came to Logan to relieve Lena as her mother’s sole nurse (Wheeler, I. 1955.) Many Christian virtues were exercised as Lena and Ida worked together to take care of their 6 small children as well as nurse their mother through her last living days. (Weyerman, L).
When November came around, Fred was preparing to leave his seriously ill mother and family of small children to fulfill a call t the German/Swiss mission, Under what he called “very hard circumstances”, he departed for Switzerland 25 November 1901. This young father knew he would not see his cherished family for over two years. (Weyerman, G). It was also likely he would never see his beloved mother again. Indeed, she died 1 December 1901, less than a week after his departure for Switzerland. The grieving family buried 4-year-old Annie E. Nuffer in the Logan City Cemetery (Utah Cemetery Inventory).
For an unknown reason, Annie made made the unusual request before she died to have their family’s temple sealing to her second husband, John Christoph Nuffer, cancelled. She wanted Fred to go to the LDS authorities and arrange for her to be sealed to her first husband, Gottfried Weiermann, and then to have their seven children sealed to them. This wish was eventually fulfilled in the Logan LDS temple on 8 March 1905, about a year after Fred returned from his mission. (Ida Christensen Arave witnessed the Church temple records at the family history center in SLC) (Wheeler, I., 1955).
Anna Elizabeth Reber’s family was one of 90,000 known Latter-day Saint immigrants who crossed the oceans to America between 1840-1891. “They had a most unusual success rate; making about 550 voyages, and losing no vessels crossing the Atlantic….These Mormon immigrants were responding to a call to gather with the righteous in a promised land, which they called Zion” (Woods, 2000 p. 74). Because of courage to act on her faith, a tenacious 3 year old divorced mother of three changed her family’s course into the future. Annie’s decision to join The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints and emigrate to the American west where she could help build the Lord’s kingdom on earth has directly influenced hundreds of her progeny. Her determination not only lifted her family out of poverty, but more importantly pioneered the way toward salvation for untold numbers of future and past generations. For this act of faith, valor, and love we praise and remember her.
EPILOGUE
John Christoph Nuffer married for the fourth time four months after Annie’s death. He lived to age 73, dying 12 April 1908 (Naef, 1990).
Fred Weyerman was suddenly killed 9 March 1935 at age 59 when the bike he was riding slipped on ice and hit a bus. He left nine surviving children and his widow, who would never remarry. His sister Ida and her family kept in touch with “Aunt Lena” and their cousins for many years after his passing. (Weyerman, G).
Ida Weierman Wheeler bore 10 children and lived to be 80. She remained a faithful member of the LDS church through a multitude of trials as her she and her husband, David, worked to eke out a living on the frontier of southeastern Idaho. Her obituary quoted her friends as saying, “She was a bulwark of strength, patience, and loving kindness to all who knew her” (Wheeler, D) (Olsen, L).
Jacob Weiermann didn’t marry until 1908, when he was 25. His wife died in the 1918 Spanish flu epidemic. Their two children, Donald and Martha, went to live with their Aunt Ida and Uncle Dave for a time (Arave, I., 2017). Jacob didn’t marry again. He worked as a miner in Nevada, and died in Utah of tuberculosis 25 January 1945 at age 61 (Weierman, J., 1945).
The Church of Jesus Christ of [Latter-day] Saints in Europe
President Joseph F. Smith visited
Zurich, Switzerland in 1906, and predicted:
“The time would come when temples to the Most High would be built in various countries of the world.”
The Bern Switzerland Temple was the first temple built where English was not the main local language. It was dedicated on 11 September 1955 (Petersen, S., 2013).